Chris Dolce
Arctic cold fronts are the king of the meteorological world when it comes to the plunging temperatures in the wake of their passage. Every year, they sweep through parts of the Lower 48 states, often ushering in the coldest temperatures of the season.
A strong blast of arctic air is on its way to much of the United States. With that in mind, here are five things to know about arctic cold fronts.
1. Incredible 24-Hour Temperature Drops
When an arctic cold front is sweeping through the country, one of the favorite maps among meteorologists is the 24-hour temperature change. You'll frequently see locations 40 or more degrees colder than the exact same time the day before.
The image below shows the 24-hour temperature changes that occurred in the Central Plains behind an arctic cold front on Nov. 29-30, 2014, at 2:30 p.m. local time. Some areas in Kansas and Nebraska saw the mercury plunge 50 to 60 degrees during that 24-hour period.
As an example, O'Neill, Nebraska, was 76 degrees at 2:55 p.m. CST on Nov. 29. The next day at 2:55 p.m., it was just 15 degrees with a wind chill of minus 2 – a 61-degree drop in the actual temperature and a 78-degree drop in the feels-like temperature.
 24-hour temperature map on the afternoon of Nov. 30, 2014. Some locations in Nebraska and Kansas were 50 to 60 degrees colder than the exact same time the day before on Nov. 29, 2015.
24-hour temperature map on the afternoon of Nov. 30, 2014. Some locations in Nebraska and Kansas were 50 to 60 degrees colder than the exact same time the day before on Nov. 29, 2015.2. Major Temperature Plunges Can Occur In Minutes
In extreme situations, the temperature drops that follow arctic cold fronts can happen in just minutes.
For this next example, we turn back the clock to Dec. 12, 1919, in Amarillo, Texas. An arctic cold front, locally known as a Blue Norther in that part of the country, swept into the Texas Panhandle town.
At noon, it was 67 degrees – pleasant for an early December day at lunchtime. Cold, northerly winds then rushed in behind the Blue Norther, dropping the temperature to 23 degrees by 1 p.m., an incredible plunge of 44 degrees in one hour.
It got even worse through the afternoon and early evening. In fact, by the time people were cleaning up from dinner around 7 p.m., it was only 1 degree above zero.
3. A Few Miles Make A Big Temperature Difference
Another aspect of arctic cold fronts that frequently draws the attention of meteorologists is the difference in temperature over short distances.
The map below shows a 44-degree temperature difference observed on the afternoon of March 4, 2015, across a span of about 120 miles between the Mississippi towns of Aberdeen (81 degrees) and Tunica (37 degrees).
 Map showing the incredible temperature contrast in Mississippi and adjacent parts of Alabama, Tennessee and Arkansas around 1:30 p.m. CT on March 4, 2015. Tunica (37 degrees) and Aberdeen (81 degrees) in Mississippi are highlighted.
Map showing the incredible temperature contrast in Mississippi and adjacent parts of Alabama, Tennessee and Arkansas around 1:30 p.m. CT on March 4, 2015. Tunica (37 degrees) and Aberdeen (81 degrees) in Mississippi are highlighted.Denver on Nov. 30, 2014, provided another striking example of the contrasts that can occur in a metro area along an arctic cold front. Areas near the foothills west of Denver were in the 50s to near 60 degrees, while east and north of Denver, it was in the 20s.
 As an arctic cold front moved southwestward into the Denver area on the morning of Nov. 30, 2014, temperatures varied wildly across the metropolitan area. Places just ahead of the front touched 60 degrees while locations just a few miles away plummeted into the 20s.
As an arctic cold front moved southwestward into the Denver area on the morning of Nov. 30, 2014, temperatures varied wildly across the metropolitan area. Places just ahead of the front touched 60 degrees while locations just a few miles away plummeted into the 20s.4. Blinding Snow Squalls
Arctic cold fronts can also be accompanied by heavy bursts of snow as they pass through an area that already has subfreezing air in place.
Those snow squalls might be brief and produce little accumulation, but they can be a hazard to travelers by dropping visibility quickly and leading to automobile pileups.
Snow on the leading edge of a reinforcing arctic front on Jan. 12, 2016, caused multi-car pileups to occur in Indiana, Ohio and Pennsylvania. The snow didn't last long in any one location but came down heavily as it passed through.
The video below shows what can happen in a snow squall and how quickly conditions can change.
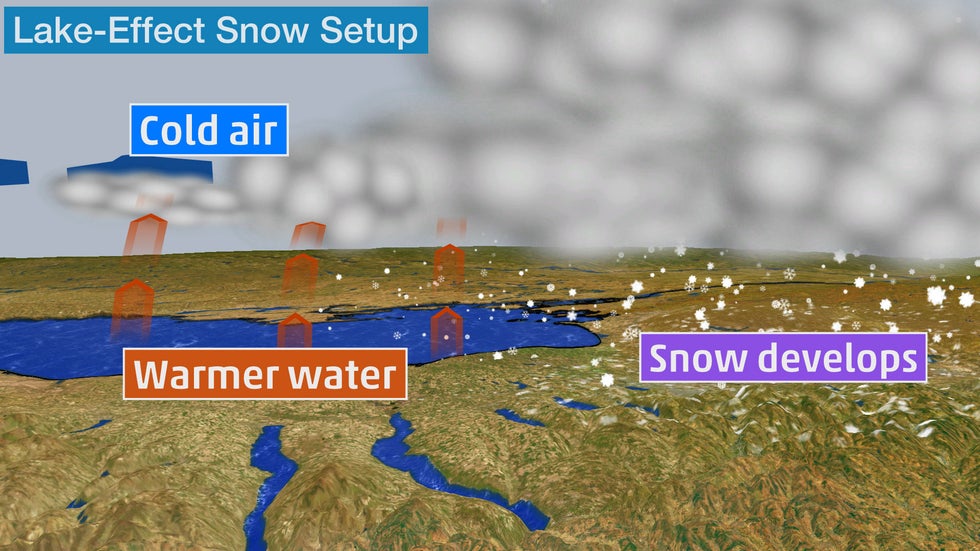
5. Kicking Off Major Lake-Effect Snow
Early in the winter season, arctic air masses sweeping across the Great Lakes often make conditions ripe for significant bouts of heavy lake-effect snow.
The frigid temperatures aloft, in contrast with the relatively warmer waters of the lakes, lead to the development of snow squalls streaming downwind of all the Great Lakes.
Sometimes, the bands of snow will be accompanied by thunder and snowfall rates of an inch or more per hour. In localized areas, snowfall totals are measured by the foot.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.

No comments:
Post a Comment