Linda Lam
Several changes in the weather typically occur in June across the Lower 48. Here's what to expect:
Atlantic Hurricane Season Officially Begins
Atlantic hurricane season officially starts June 1, although it has started early the last seven years, including this year. Tropical Storm Ana was a brief system that developed May 22.
On average in the Atlantic Basic, one named storm forms every one to two years in June and a hurricane develops about once every five years.
Early in the season, tropical systems tend to form close to the U.S. and often affect the Southeastern U.S., the western Caribbean and parts of Central America. Rainfall, rather than wind, is usually the biggest concern with June tropical cyclones.
(MORE: Here's What to Expect in June and July in Hurricane Season)
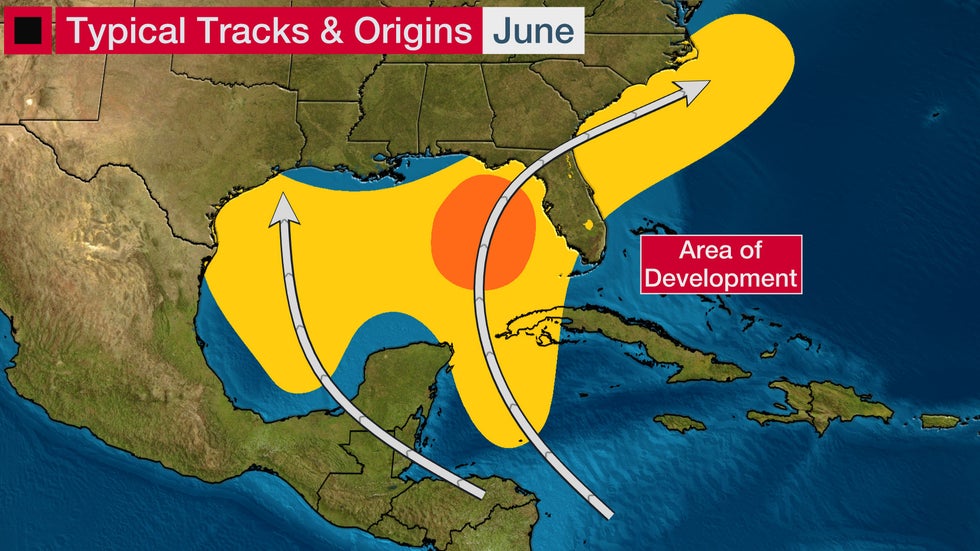
Tropical Storm Allison in 2001 and Hurricane Agnes in 1972 are two of the more notable June storms.
Allison made landfall as a tropical storm with 50 mph winds near Freeport, Texas, and quickly weakened to a tropical depression. However, it lingered for days in the Houston metro area and caused severe flooding.
Agnes made landfall in Florida, but it curled northwestward toward New York City as a tropical storm and stalled over the Northeast, where it dumped flooding rain.
Tornado Threat Shifts Northward
June is typically an active month for tornadoes. Tornadoes can happen just about anywhere in the Lower 48 in June, given the widespread warmth and humidity.
Low pressure systems can create the ingredients for severe weather in the Plains and Midwest, in particular. The area at greatest risk of tornadoes in June stretches from central Oklahoma into southwestern Minnesota.
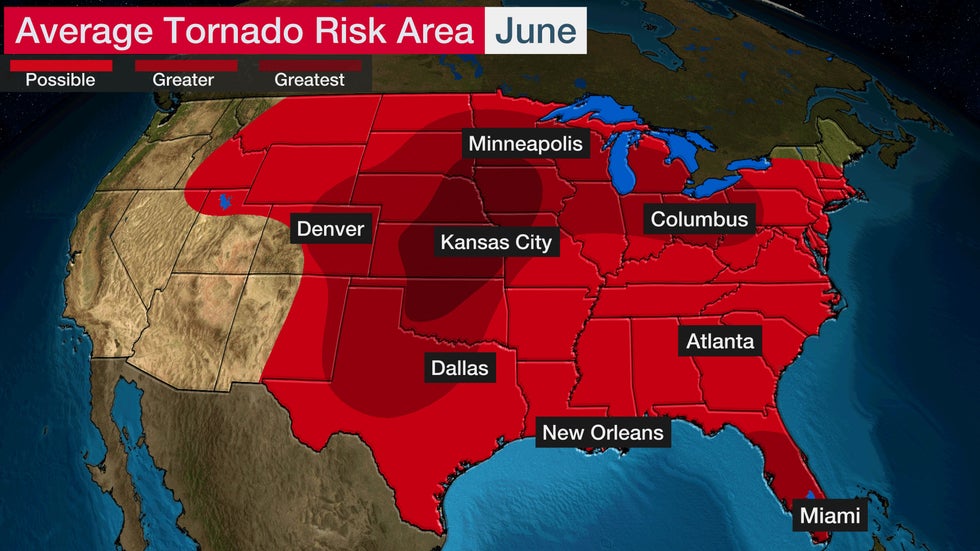
Brief, usually weaker tornadoes often occur near the Gulf Coast during the summer. These are usually caused by sea-breeze thunderstorms and sea breeze collisions closer to the coast. Scattered thunderstorms can also create brief tornadoes across much of the South.
Tropical systems can also bring tornadoes, although they are usually weak and short-lived.
Peak hail activity also occurs in June, according to some studies. The Central and Southern Plains see an increase in hail during the early summer due to the combination of the jet stream, moisture from the Gulf of Mexico and daytime heating.
Thunderstorms, Lightning and Flash Flooding Increase
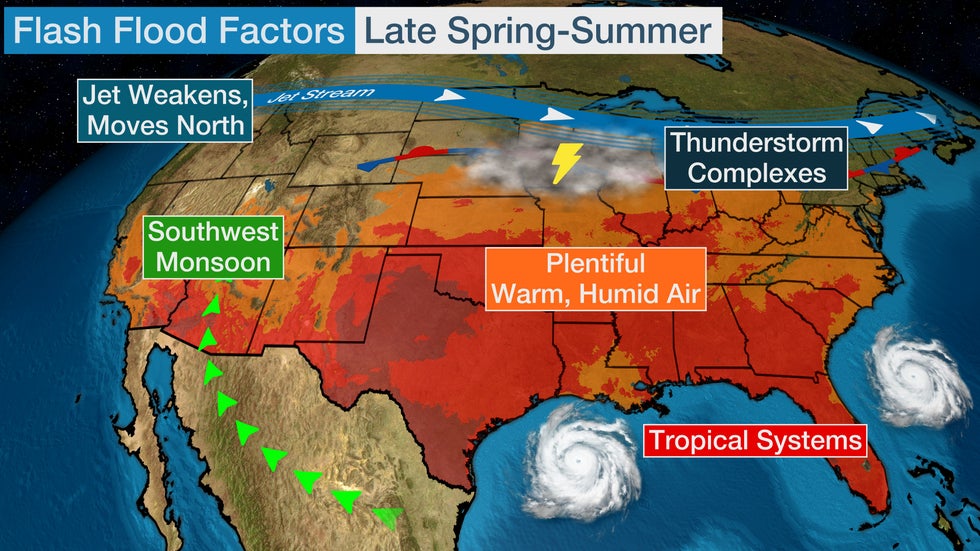
Warm, moist air expands in June, bringing daily pop-up thunderstorms to much of the East, South and Midwest. Clusters of thunderstorms, also called Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS), often track across portions of the Central Plains into the Ohio and Tennessee Valleys during the afternoon and overnight hours.
Lightning can accompany both pop-up and long-track thunderstorms. Lightning can strike as far as 15 miles away from its parent thunderstorm, so it is important to be weather aware during the summer months. June has the second-most lightning-related deaths. July has the most.
Because moisture across the U.S. in June, thunderstorms become more efficient rainfall producers. The weakening jet stream can lead to slow-moving systems. Both factors increase the concern for flash flooding during the summer months. Tropical systems can also bring heavy rainfall and flooding.
Monsoon season, with increased chances for thunderstorms and flash flooding, begins in the Southwest on June 15.
Temperatures Heat Up
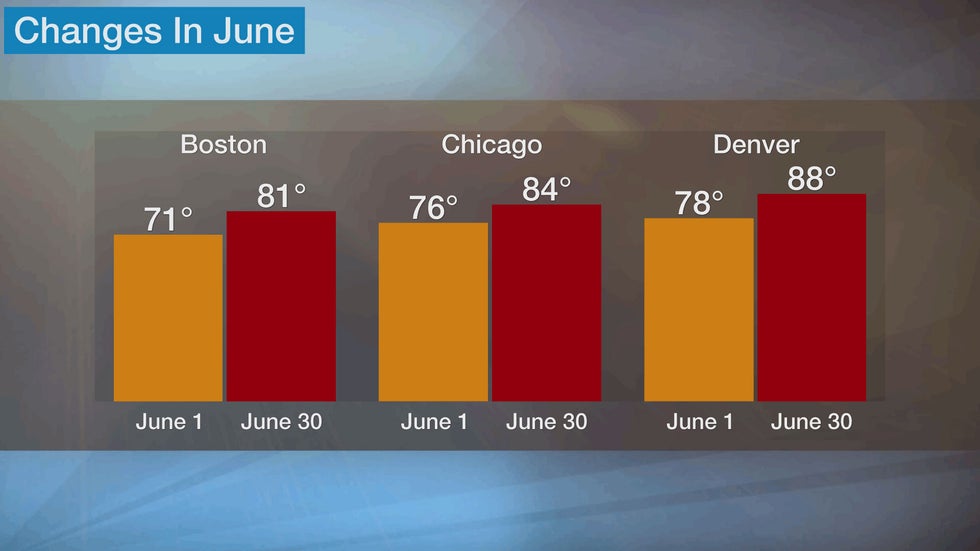
Temperatures and humidity levels increase across the U.S. in June.
In early June, average high temperatures from Boston to New York are in the 70s and rise into the 80s by the end of the month. The average low in Washington, D.C. on June 1 is 63 degrees and climbs to 71 degrees by June 30.
Chicago and Minneapolis experience average highs in the mid-70s in early June and reach the mid-80s by the start of July. Lows average in the mid-60s for much of the Midwest by late June.
Dallas experiences average highs in the mid-90s by the end of June. Lows in the 70s are common by the end of the month across most of the South.
The average high in Denver jumps by 10 degrees during June and the average low rises from 49 degrees on June 1 to 57 degrees on June 30. The average high by the month's end is 107 degrees in Phoenix and 91 degrees in Sacramento, with an average low of 83 degrees and 58 degrees, respectively.
June Gloom Arrives in California
June gloom refers to when the temperature drops and low clouds and fog move ashore during the morning hours in parts of Central and Southern California.
Cold, more humid air comes from the chilly ocean current that can be pushed onshore due to a pressure gradient that develops. This pressure gradient is from the combination of an area of high pressure located off the California Coast and a thermal low that develops inland due to intense heating.
Low clouds form and are pushed onto the beaches. The marine layer can be deep enough at times that light rain showers develop.
Clouds usually clear by early afternoon as heating scours out the cold oceanic air.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.

No comments:
Post a Comment