Jonathan Erdman
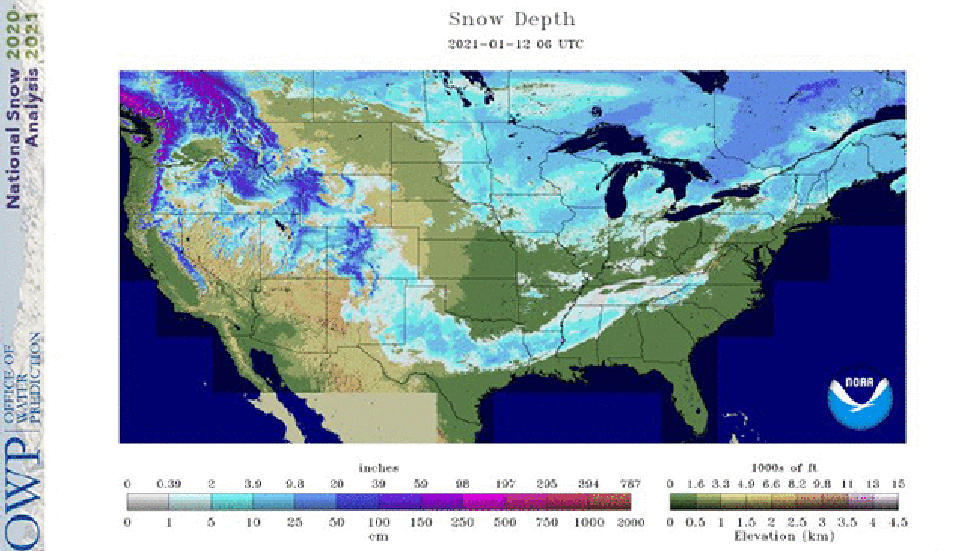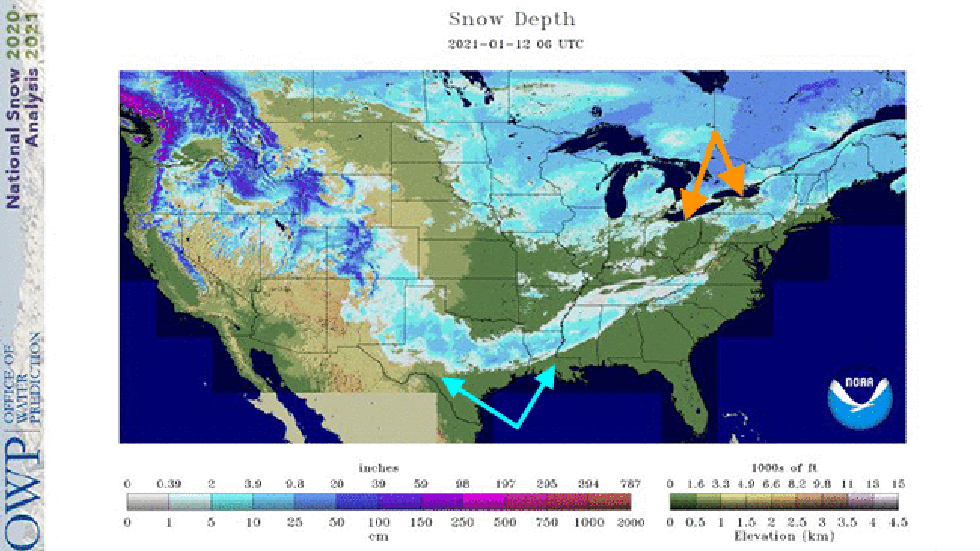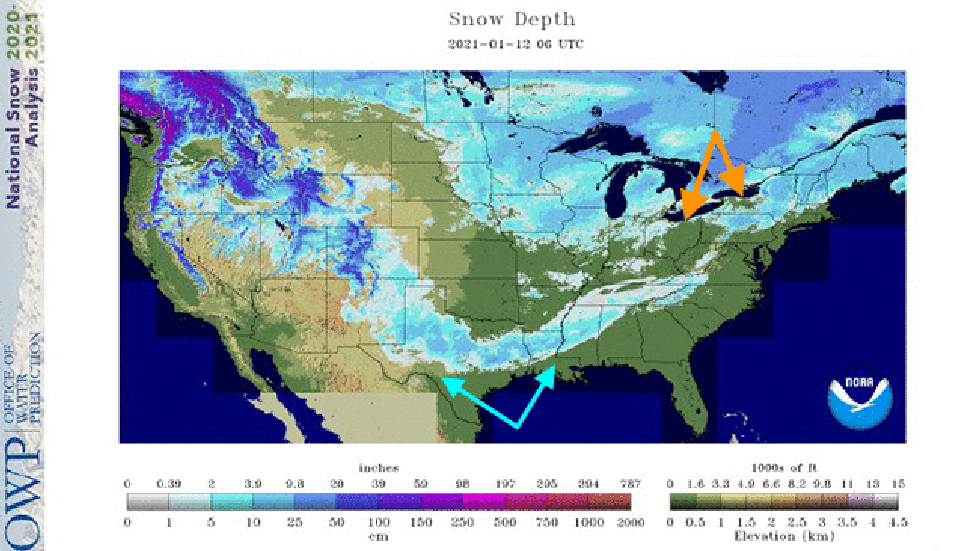 A satellite snow depth analysis on Jan. 12, 2021, shows snow cover left from a southern winter storm from Texas into the Deep South (highlighted by the teal arrows) while parts of the Great Lakes snowbelts were snowless (highlighted by the orange arrows).
A satellite snow depth analysis on Jan. 12, 2021, shows snow cover left from a southern winter storm from Texas into the Deep South (highlighted by the teal arrows) while parts of the Great Lakes snowbelts were snowless (highlighted by the orange arrows).Snow was either strangely present or absent by mid-January standards in some parts of the country this week, which made for an interesting snow cover analysis map.
Meteorologists examine current snow depth maps for a number of reasons, like mapping out snowfall from recent winter storms, monitoring areas for flood risk due to melting snow and even temperature forecasting.
SPONSORED: Shop sale on winter best sellers at UNIQLO
Tuesday morning's snow cover analysis from NOAA's National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center (NOHRSC) was odd in several ways.
Southern Snow Footprint
Snow in parts of the South isn't all that unusual in winter. Areas from central Texas to the coastal Carolinas average at least a tenth of an inch of snow each winter.
But the recent winter storm over the South wasn't just a dusting.
Several locations from far southeastern New Mexico into western, central and eastern Texas, northern Louisiana and Mississippi were blanketed by at least 6 inches of snow. Waco, Texas, had its heaviest snowstorm (4.4 inches) in 38 years. Trees were downed and power was knocked out to more than 150,000 customers in Texas and Louisiana.
More than 24 hours after the storm was over, satellite imagery Tuesday still showed snow on the ground in parts of East Texas and northern Louisiana.
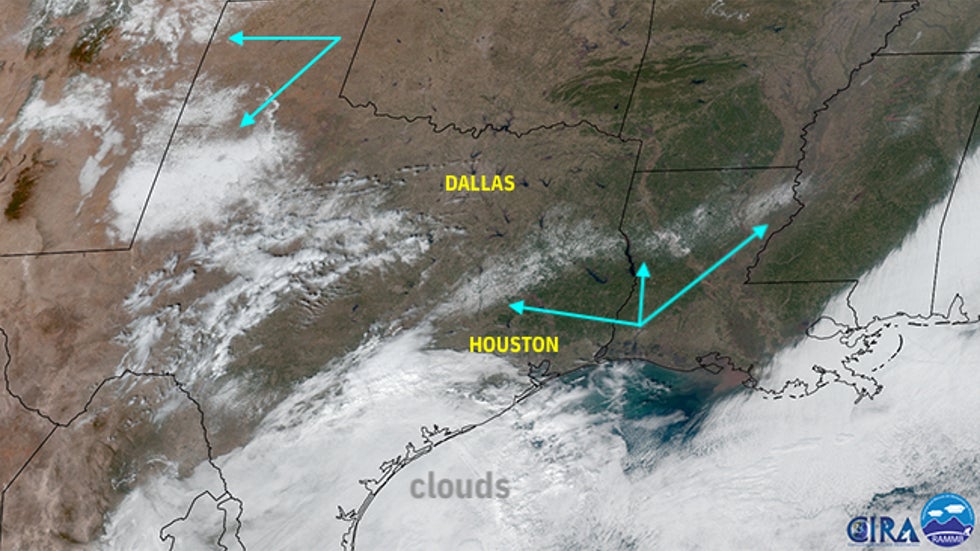 This visible satellite image from GOES-East shows leftover snow cover, highlighted by the teal arrows, from eastern Texas into Louisiana, and also over parts of West Texas into New Mexico on Jan. 12, 2021. Most other areas of white on this satellite image were clouds.
This visible satellite image from GOES-East shows leftover snow cover, highlighted by the teal arrows, from eastern Texas into Louisiana, and also over parts of West Texas into New Mexico on Jan. 12, 2021. Most other areas of white on this satellite image were clouds.Great Lakes Lacking
While parts of Texas and Louisiana were still melting their snowpack, parts of the infamously snowy Great Lakes had no snow on the ground.
While some snowbelt areas between these observing sites still had at least some snow on the ground, no measurable snow cover was reported Tuesday at the official observation sites in Buffalo, Cleveland, Erie and Syracuse.
The fact that all four of these notoriously snowy cities had no measurable snow cover at the same time was impressive for mid-January; Annual average snowfall ranges from 67 inches in Cleveland to 124 inches in Syracuse.
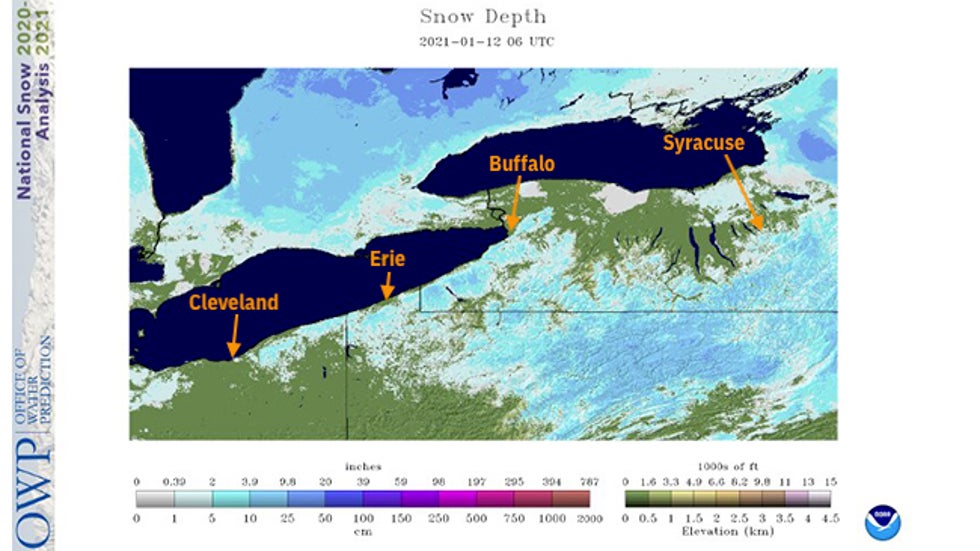 The same satellite snow depth analysis on Jan. 12, 2021, but this time zoomed in over the eastern Great Lakes, showed snow cover lacking in Cleveland, Erie, Pennsylvania, Buffalo, and Syracuse, New York, labeled by orange arrows.
The same satellite snow depth analysis on Jan. 12, 2021, but this time zoomed in over the eastern Great Lakes, showed snow cover lacking in Cleveland, Erie, Pennsylvania, Buffalo, and Syracuse, New York, labeled by orange arrows.In fact, if you ignored the timestamp and looked at only the photo tweeted out last Saturday by 3News meteorologist Matt Standridge, you'd be hard-pressed to guess it was January in downtown Cleveland, with green grass and sunshine.
Another usually reliably snowy Great Lakes snowbelt city, Grand Rapids, Michigan, has had its least snowy start to a winter season in 115 years, according to the National Weather Service.
A Christmas snowstorm hammered the eastern Great Lakes with almost 2 feet of snow in Buffalo, almost 19 inches in Erie and 10 inches of snow in Cleveland.
Since then, it hasn't been very cold.
In Cleveland, the temperature rocketed into the middle 40s immediately after the Christmas storm, quickly melting the holiday snow.
In Buffalo, rain and warmer temperatures obliterated the Christmas snow cover by New Year's Day.
And the parts of the Midwest and Northeast with snow on the ground don't have a terribly impressive snowpack for mid-January.
The map below showing how far above and below average the snow depth is right now almost looks "upside-down".
Most of the northern U.S. has below-average snowpack while, due to the recent snowstorm, that strip of the South, of course, has above-average snowpack.
This milder recent pattern in the Great Lakes was due to a sprawling dome of high pressure aloft which extended west from near Greenland across central and eastern Canada, brushing the nation's northern tier and squeezing the storm track to the southern U.S., giving rise to the Southern snow.
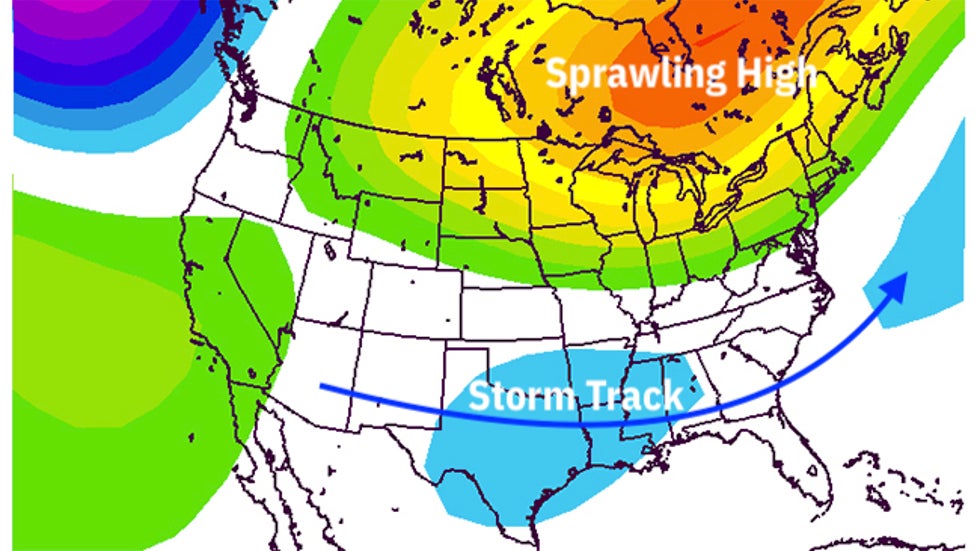 Contoured above are anomalies in the 500-millibar (mid-levels of the atmosphere) pattern through the first 10 days of 2021. Shades of yellow and orange denote the expansive dome of high pressure aloft which kept the Great Lakes relatively mild but also pushed the storm track into the South.
Contoured above are anomalies in the 500-millibar (mid-levels of the atmosphere) pattern through the first 10 days of 2021. Shades of yellow and orange denote the expansive dome of high pressure aloft which kept the Great Lakes relatively mild but also pushed the storm track into the South.It was the coexistence of a January thaw in the nation's northern tier and a South snowstorm that produced this weird snow cover map.
It won't last long.
South snow cover typically melts within a couple of days, as temperatures warm back into the 40s and 50s, if not warmer. And it's only a matter of time before snow returns to the Great Lakes snowbelts.
Buffalo was expecting light lake-effect snow Tuesday. And in Cleveland, over 60% of snow in an average winter season falls after Jan. 12.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.

No comments:
Post a Comment