The 2020 Atlantic hurricane season has already produced two named storms before June 1, and past similar years suggest this is at least somewhat suggestive of an active season ahead.
Tropical Storm Bertha spun up Wednesday morning off the South Carolina coast before quickly making a landfall northeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
Less than two weeks ago, Tropical Storm Arthur brushed eastern North Carolina.
(MORE: 2020 Atlantic Hurricane Season Outlook)
 The tracks of the two May 2020 Atlantic Basin tropical storms, Arthur and Bertha, as of late morning on May 27, 2020.
The tracks of the two May 2020 Atlantic Basin tropical storms, Arthur and Bertha, as of late morning on May 27, 2020.While it's the sixth straight hurricane season that started early, meaning at least one named storm formed before the official June 1 start, far fewer seasons have delivered two such storms this early.
According to Colorado State University tropical scientist Phil Klotzbach, only five other years in records dating to 1851 produced two storms before June 1.
The most recent was in 2016, when a bizarre January Hurricane Alex in the eastern Atlantic Ocean was followed by a late May Tropical Storm Bonnie off the Southeast coast.
The other recent season was in 2012, when a pair of May tropical storms, Alberto and Beryl, spun up off the Southeast coast in a similar area as this year's Arthur and Bertha.
 2012 Atlantic hurricane season tracks in May, then tracks over the rest of the season, including notable U.S. landfalls.
2012 Atlantic hurricane season tracks in May, then tracks over the rest of the season, including notable U.S. landfalls.Any Signal in Early Activity?
Admittedly, five years out of a 169-year database isn't a very large sample size to make definitive conclusions.
Also, despite the considerable effort of the Atlantic Hurricane Database Re-analysis Project, there may have been some storms missed in the era before satellites routinely scanned the Atlantic Basin starting in the mid-1960s.
With that in mind, let's take a look at those five seasons.
Three of the five previous seasons in which two storms formed prior to June 1 had an above-average number of storms and hurricanes.
Those five seasons combined typically produced two more named storms and one more hurricane than the 30-year average. That makes sense. One essentially is getting a two-storm headstart on the season, right?
 Number of storms, hurricanes and those hurricanes of Category 3 or stronger intensity in the five previous seasons that had two named storms before June 1.
Number of storms, hurricanes and those hurricanes of Category 3 or stronger intensity in the five previous seasons that had two named storms before June 1.Only two of those five seasons were above average for Category 3 or stronger hurricanes, however.
Let's look at another metric of season activity, known as the ACE index. Meteorologists generally prefer to use the ACE index to rank seasons and individual hurricanes as well.
ACE – an acronym for accumulated cyclone energy – is calculated by summing up each tropical storm or hurricane's wind speed over its lifetime. Long-lived, intense hurricanes have a high ACE index, while brief, weak tropical storms have a low ACE index. Compiling each storm or hurricane's ACE index gives you a measure of how active the hurricane season was.
Four of the five previous hurricane seasons with two pre-June 1 storms went on to register above-average ACE for the entire season. The 1887 season ended up just shy of the 10 highest seasonal ACE totals.
 ACE index of the five Atlantic hurricane seasons in which two storms formed prior to June 1. The bar at the far right is the 30-year average ACE index.
ACE index of the five Atlantic hurricane seasons in which two storms formed prior to June 1. The bar at the far right is the 30-year average ACE index.In an earlier piece, we examined the 10 most active hurricane seasons by ACE and found only two of them had a storm in May or earlier: 1933 and 2017.
So, there is modest support, at best, among a limited dataset for a more active season ahead, given the two early storms.
As Klotzbach pointed out during Arthur, there is little correlation between the date of the first storm of the season and the entire season's activity since the mid-1960s.
Should Hurricane Season Start Earlier?
Given Arthur made this the sixth season in a row with a preseason named storm, this prompted some discussion among meteorologists about whether the Atlantic hurricane season should start in May, rather than June.
The short answer to this was summed up nicely in a Forbes piece from Dr. Marshall Shepherd of the University of Georgia.
June 1 seems to fit the lion's share of the data nicely.
FEMA atmospheric scientist Michael Lowry pointed out June through November captures 99 percent of all Atlantic hurricane activity.
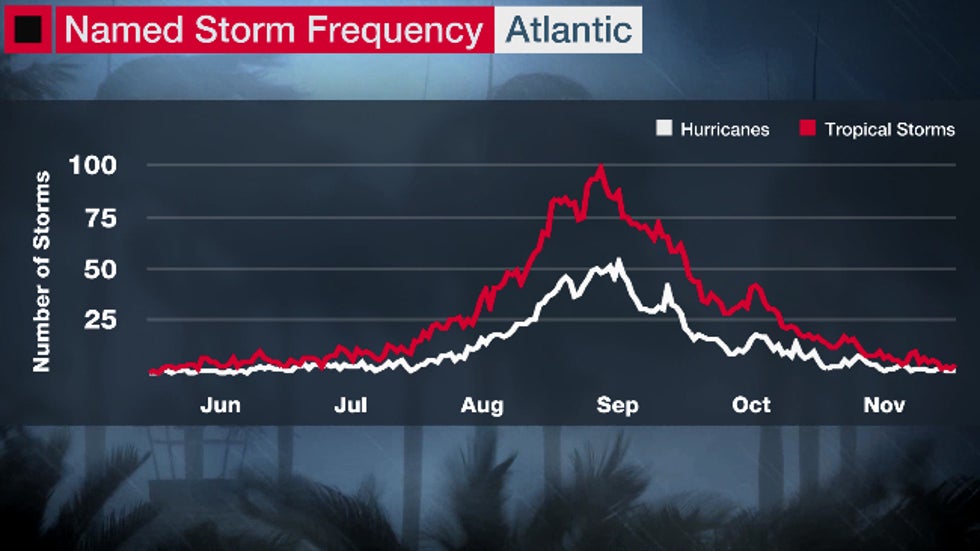 The typical frequency of named storms (in red) and hurricanes (in white) by month in the Atlantic Basin.
The typical frequency of named storms (in red) and hurricanes (in white) by month in the Atlantic Basin.Sam Lillo, a NOAA researcher at the University of Colorado, found little change in the number of May storms since the mid-20th century.
And, of course, what ultimately matters aren't simply numbers of named storms and hurricanes, but where they go and what they hit.
Hurricanes Matthew and Hermine struck the U.S. in 2016. Superstorm Sandy and Hurricane Isaac both made a U.S. landfall in 2012. Three Category 1 hurricanes made landfall in 1887. However, 1951, another year with two pre-June 1 storms, had no U.S. hurricane landfalls.
While there is no correlation between the number of storms and the number of landfalls in a season, Klotzbach noted 96 percent of Category 3 or stronger continental U.S. hurricane landfalls have occurred between August and October.
So this is the time to develop or review your hurricane plan, well before a storm or hurricane is on the horizon.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.

No comments:
Post a Comment