Russian meteorologists have confirmed a Siberian town smashed its all-time record high during a June heat wave, possibly the hottest temperature on record so far north in the Arctic, continuing an off-the-charts warm year in what is typically one of coldest places on Earth.
On June 20, the high temperature in Verkhoyansk, a town in northeast Russia about 260 miles south of the Arctic coast and about 6 miles north of the Arctic Circle, topped out at 38 degrees Celsius, or 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
This extreme temperature was confirmed by the Russian Federal Service for Hydrometeorological and Environmental Monitoring after a request from the World Meteorological Organization, topping the city's previous record set on July 25, 1988. Temperature records in Verkhoyansk date to 1885.
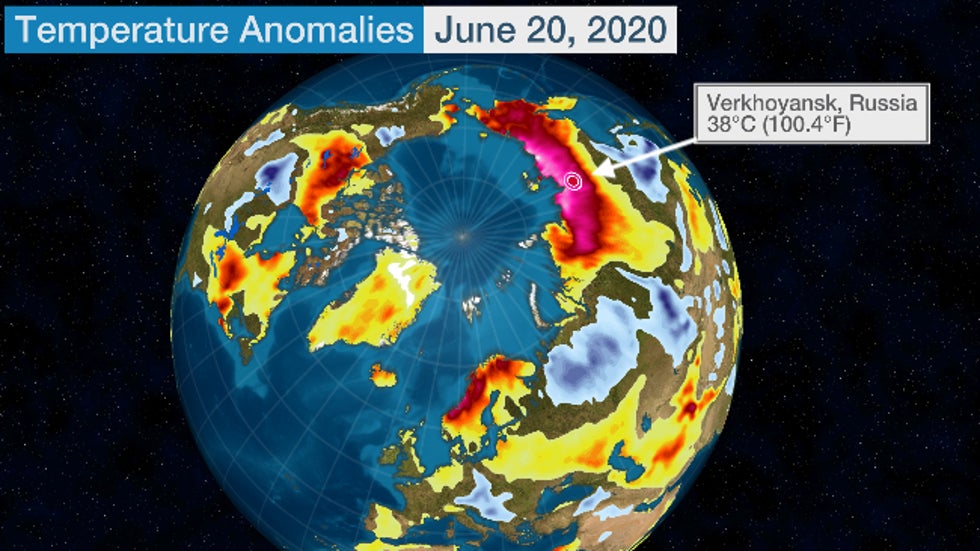
It may also have been the hottest temperature on record north of the Arctic Circle, according to Etienne Kapikian, a meteorologist with Meteo France.
The average high in late June in Verkhoyansk is only in the upper 60s, or around 20 degrees Celsius.
Let that soak in for a moment.
Siberia, one of the world's coldest places in winter, reached 100 degrees (F) this year before Dallas or Houston did.
To escape the heat, children were seen swimming in a lake near Verkhoyansk, Sunday, a lake that would be frozen solid in the depths of winter, when average temperatures in Russia's "Pole of Cold" typically plunge into the minus 40s and 50s Celsius.
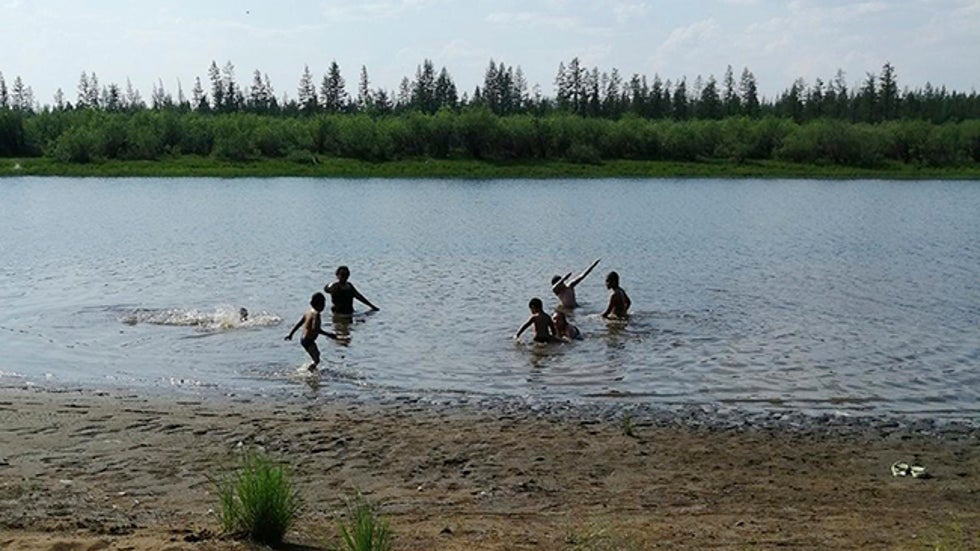 In this handout photo provided by Olga Burtseva, children play in the Krugloe lake outside Verkhoyansk, the Sakha Republic, about 4660 kilometers (2900 miles) northeast of Moscow, Russia, Sunday, June 21, 2020.
In this handout photo provided by Olga Burtseva, children play in the Krugloe lake outside Verkhoyansk, the Sakha Republic, about 4660 kilometers (2900 miles) northeast of Moscow, Russia, Sunday, June 21, 2020.Verkhoyansk once plunged to minus 67.8 degree Celsius - minus 90 degrees Fahrenheit - on Feb. 5 and 7, 1892.
This is 105.8 degrees Celsius colder than its just-recorded all-time record high. That's a difference in extremes larger than the difference between water's freezing and boiling points, likely the largest spread between all-time record high and low temperatures anywhere on Earth.
That wasn't the only eye-popping extreme of this June Russian heat wave.
Ten days later, Ust'-Olenek, Russia, soared to 34.3 degrees Celsius (93.7 degrees Fahrenheit). The average high temperatures, there, are only around 10 to 12 degrees Celsius (50 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit), according to meteorologist Scott Duncan.
This town on Russia's Arctic coast about 2,500 miles northeast of Moscow and over 400 miles north of the Arctic Circle may have registered the farthest north Arctic 90-degree temperature on record, according to an analysis by Alaska-based climatologist Brian Brettschneider.
The following day, Ust'-Olenek only dropped to a low of 22.6 degrees Celsius (72.7 degrees Fahrenheit), on par with an average low temperature in parts of the United States in July.
Expansive blocking high pressure aloft over Siberia was responsible for this latest heat wave, which has been in place since mid-June.
This blocking high hasn't allowed colder air to push south from Russia's Arctic coast.
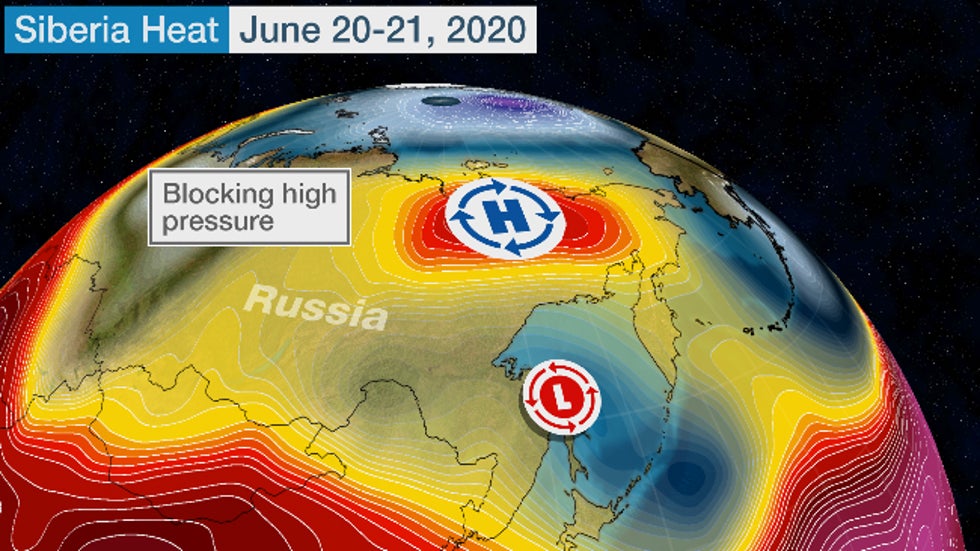 The blocking high-pressure ridge responsible for record heat in Siberia on June 20-21, 2020.
The blocking high-pressure ridge responsible for record heat in Siberia on June 20-21, 2020.And this is continuing a trend so far in 2020.
Berkeley Earth lead scientist Robert Rohde noted Russia clobbered its record warmest January - May period in 2020 by a whopping 1.9 degrees Celsius over the previous record warmest first five months of a year, 2016.
By far and away, Russia has been the epicenter of the planet's most expansive and extreme warm anomalies in 2020.
"It has been an unusually hot spring in Siberia, and the coinciding lack of underlying snow in the region combined with overall global temperature increases, undoubtedly helped play a critical role in causing this extreme temperature observation," said Randall Cerveny, extreme weather expert for the World Meteorological Organization in a June 23 initial press release on the Verkhoyansk temperature.
The persistent warm and dry weather fueled wildfires which already began scorching parts of northern Russia in April and are continuing to burn in this latest heat wave.
A diesel fuel spill earlier in June in Norilsk, Russia, was found to be caused by supporting pillars of a storage tank sinking into thawing permafrost, causing the tank to collapse.
It's also no surprise Arctic sea ice coverage along the coast of Siberia is also at a 41-year record low for this time of year, as pointed out by climate scientist Zach Labe.
Even more troubling is these temperatures appear to be occurring decades ahead of climate change projections, according to climate specialist Jeff Berardelli.
The Arctic appears to be warming three times faster than the rest of the planet, according to NASA climate scientist Gavin Schmidt.
And a just-released study utilizing reconstructions of ancient temperatures found current global temperatures are the warmest in at least 12,000 years, if not longer.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.
The Weather Company’s primary journalistic mission is to report on breaking weather news, the environment and the importance of science to our lives. This story does not necessarily represent the position of our parent company, IBM.

No comments:
Post a Comment